Samsung (KRX:005930) is a multinational corporation headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, known worldwide for its cutting-edge technology and innovations. Since its establishment in 1938, Samsung has evolved from a small trading company to one of most popular technology corporations globally. Yet, equally significant, albeit less publicized, is its active engagement and collaboration with other Asian nations. This cooperation plays a pivotal role in both Samsung’s development and the economies of the Asian region.
The company has been actively investing in manufacturing facilities, research and development, and education across Asia for decades. The corporation has placed its factories and research centers in countries such as China, India, Vietnam and Indonesia, leveraging local labor markets, production chains, burgeoning demand for machinery.
In the last 10 years, there has been a notable expansion trend in Southeast Asia. Countries such as Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia are emerging as important partners for Samsung as it aims to diversify its manufacturing base and reduce reliance on the Chinese economy. In Vietnam, for example, Samsung stands as one of the largest foreign investors and employers, significantly contributing to the country’s exports and job opportunities.
Moreover, like many other high-tech companies, Samsung has set its sight on India. The corporation places considerable importance on the Indian market by opening the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturing plant in Noida in 2018. The company also invests in research centers and digital learning programs, supporting local talent development and the country’s digitalization.
In recent years, Samsung has significantly increased its presence in the Chinese market by investing in production lines for smartphones, semiconductors, and consumer electronics. However, due to increased competition from local manufacturers and shifting geopolitical trends, the company faces the challenge of strategic reorganization. For example, with the release of the new flagship smartphones of the Galaxy S24 series to the Chinese market, the company collaborated with the local search giant Baidu (NASDAQ:BIDU) to integrate specialized services. Although this partnership signals Samsung’s long-term commitment to business development in China, it may not yield significant profits immediately. Some Chinese customers have expressed concerns about the functionality of Baidu’s services compared to Google’s offerings on the international version of Galaxy S24 smartphones.
Samsung is investing in manufacturing and taking on social responsibility in the region. It launches various educational and social programs, such as the Samsung Hope Project, which aims to support youth and communities in unlocking their potential.
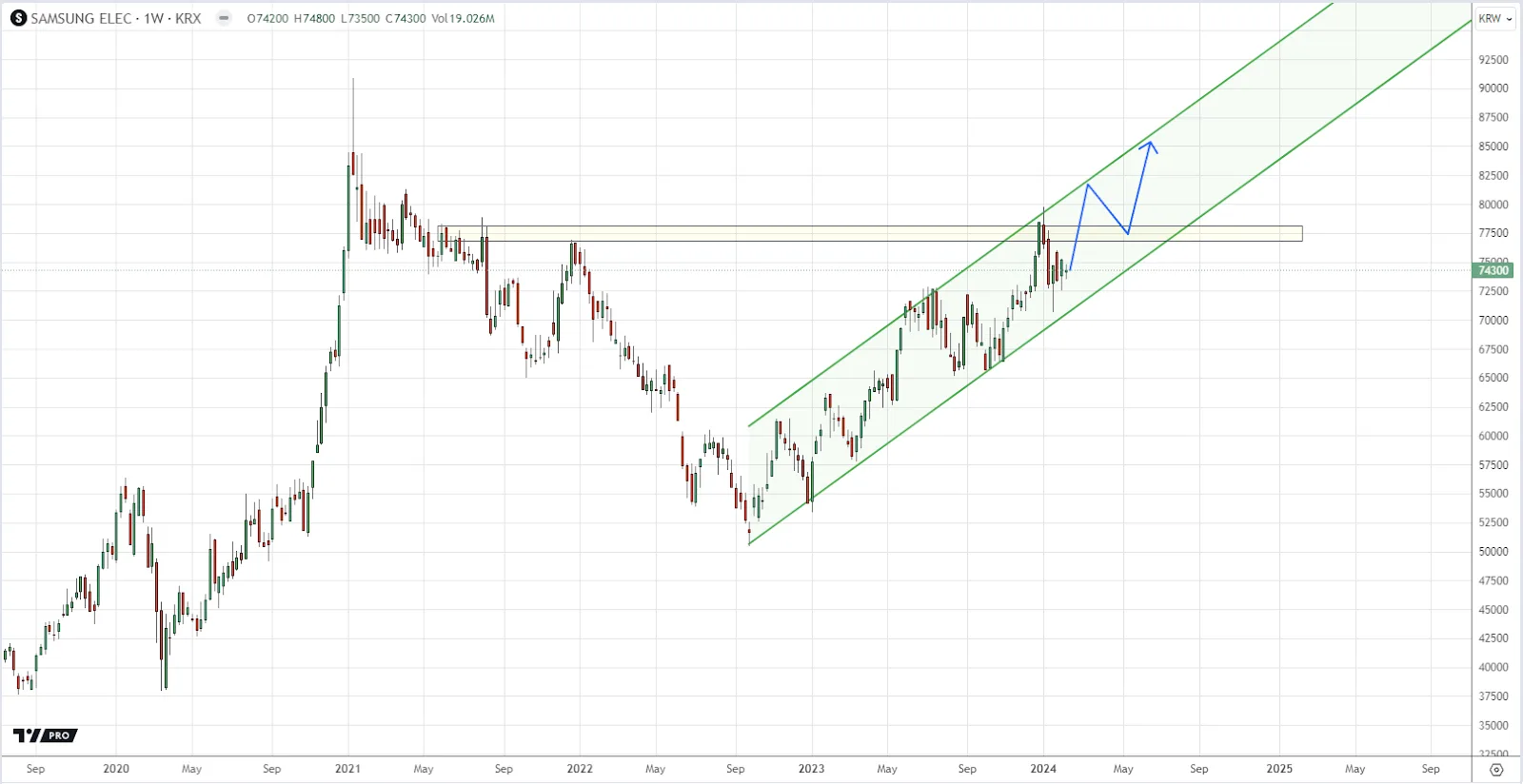
Over time, investors have consistently paid higher prices for Samsung Electronics stock, indicating a rising trend channel in the medium to long term. This suggests growing optimism among investors and implies a sustained upward trajectory. Currently, the stock is trading within a rectangle formation, with support and resistance indicator standing at 979 and 1242 respectively. A clear breakout above or below these levels will determine the stock’s new direction.
Samsung’s cooperation with Asia is an example of a global corporation attuned to local economic conditions and cultural nuances. This dynamic interaction accelerates the growth and innovation of both Samsung and the Asian region, fostering stronger technological, economic, and cultural ties across borders. Although each new step of the company is carefully weighed in the context of global politics and marketing strategies, there is no doubt that Samsung and Asia will continue to strengthen their cooperation in advancing technological progress and shared prosperity.



